Facial Trauma
Oral and maxillofacial surgeons are trained, skilled and uniquely qualified to manage and treat facial trauma. Injuries to the face, by their very nature, impart a high degree of emotional, as well as physical trauma to patients. The science and art of treating these injuries requires special training involving a “hands on” experience and an understanding of how the treatment provided will influence the patient’s long term function and appearance.
The Nature Of Maxillofacial Trauma
There are a number of possible causes of facial trauma such as motor vehicle accidents, accidental falls, sports injuries, interpersonal violence, and work-related injuries. Types of facial injuries can range from injuries of teeth to extremely severe injuries of the skin and bones of the face. Typically, facial injuries are classified as either soft tissue injuries (skin and gums), bone injuries (fractures), or injuries to special regions (such as the eyes, facial nerves or the salivary glands).
Soft Tissue Injuries Of The Maxillofacial Region
When soft tissue injuries such as lacerations occur on the face, they are repaired by suturing. In addition to the obvious concern of providing a repair that yields the best cosmetic result possible, care is taken to inspect for and treat injuries to structures such as facial nerves, salivary glands, and salivary ducts.
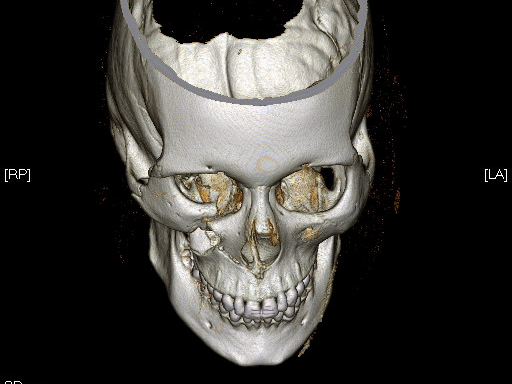
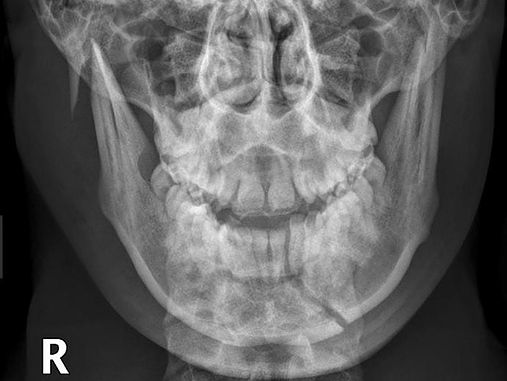
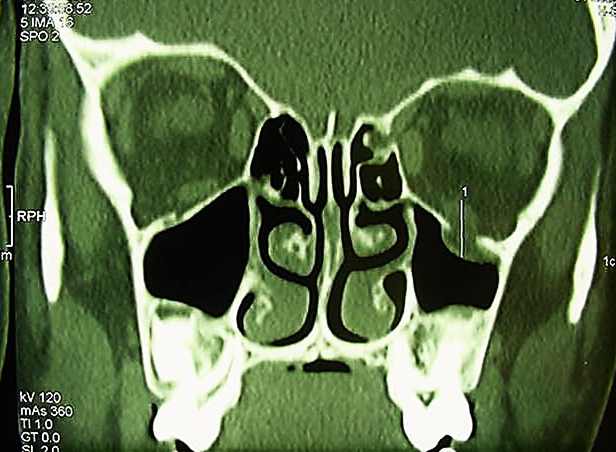
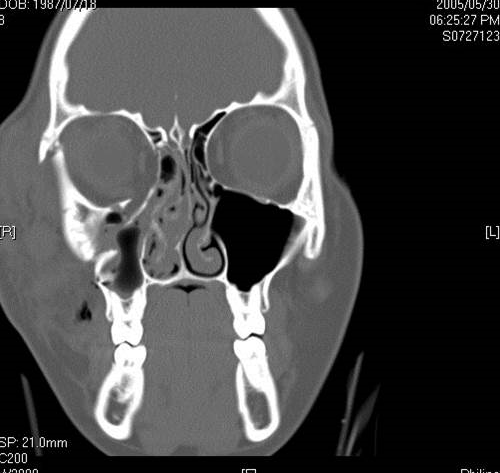
Bone Injuries Of The Maxillofacial Region
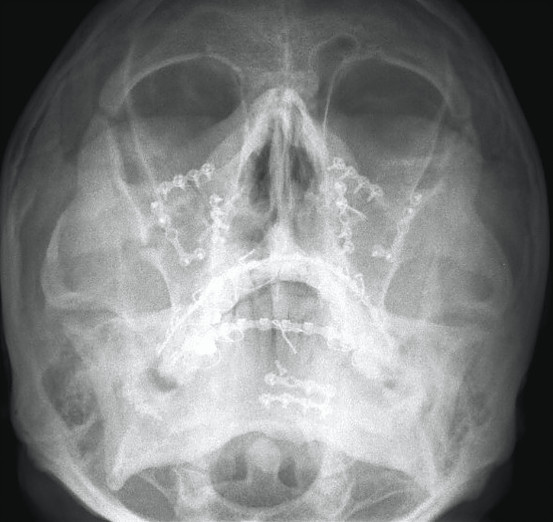
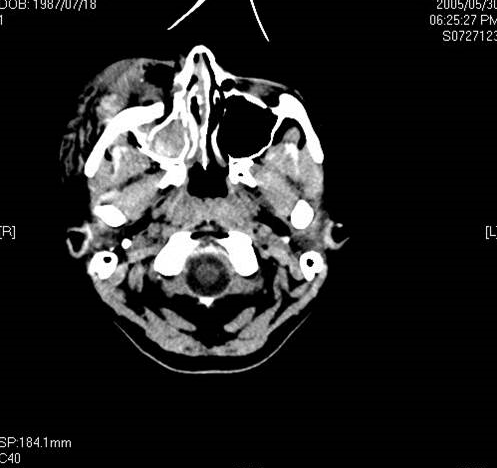
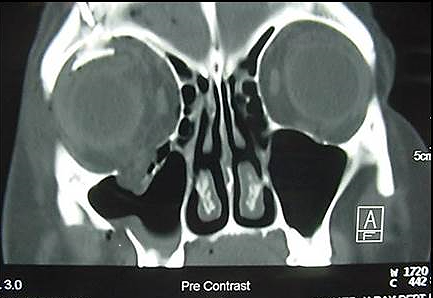
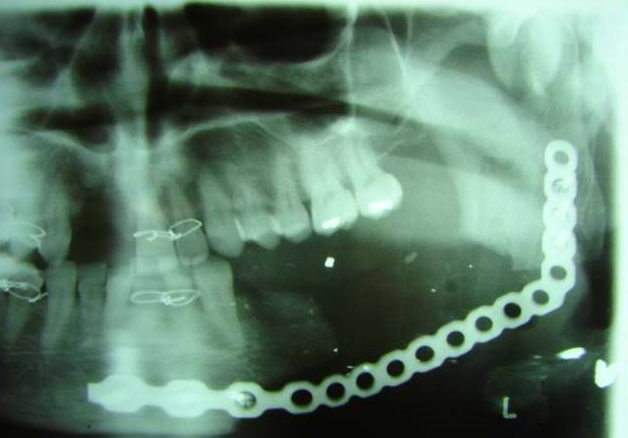
Fractures of the bones of the face are treated in a manner similar to the fractures in other parts of the body. The specific form of treatment is determined by various factors, which include the location of the fracture, the severity of the fracture, the age, and general health of the patient. When an arm or a leg is fractured, a cast is often applied to stabilize the bone to allow for proper healing. Since a cast cannot be placed on the face, other means have been developed to stabilize facial fractures.
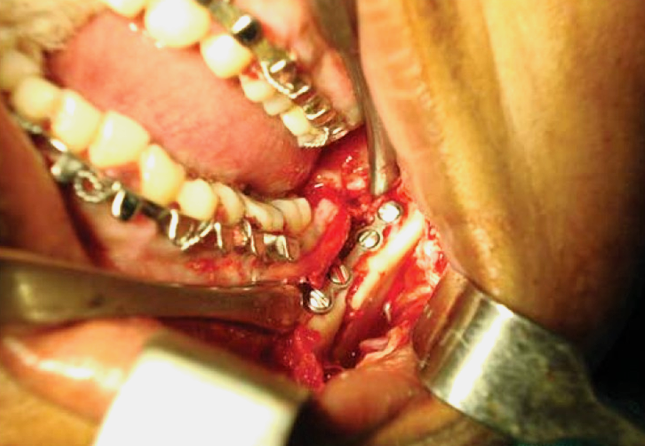
One of these options involves wiring the jaws together and this was the mainstay of treatment in the past. Nowadays, fractures of the jaw are best treated and stabilized by the surgical placement of small plates and screws at the involved site allowing for rigid fixation of the fracture. The development and use of rigid fixation has profoundly improved the recovery period for many patients, allowing them to return to normal function more quickly.
The treatment of facial fractures should be accomplished in a thorough and predictable manner. More importantly, the patient’s facial appearance should be minimally affected. An attempt at accessing the facial bones through the fewest incisions necessary is always made and many approaches are possible from within the mouth. The skin incisions that become necessary, are designed to be small and in natural creases so that the resultant scar is hidden.